Building the Future: Diverse 3D Printing Applications
Revolutionizing Manufacturing Processes
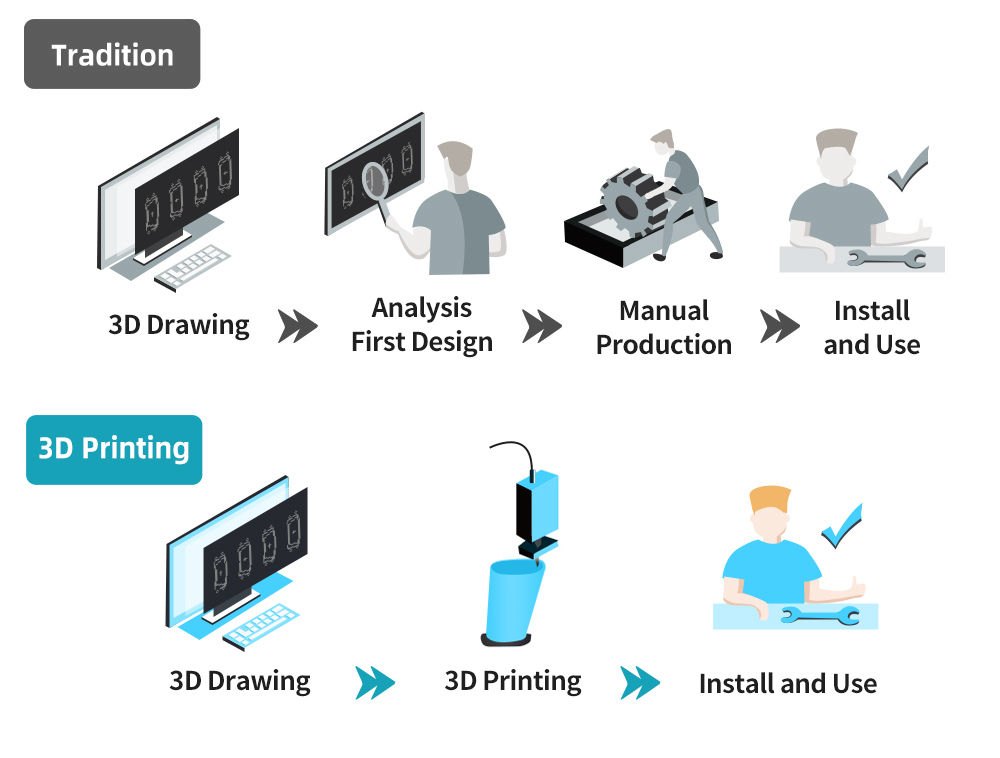
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a revolutionary force in the manufacturing industry. Traditional manufacturing methods are being redefined as 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate and complex structures layer by layer. This transformative technology is unlocking new possibilities and efficiencies across various industries.
To explore further insights into 3D printing applications, visit 3D printing applications.
Medical Breakthroughs through Bioprinting
One of the most remarkable applications of 3D printing is in the field of medicine through bioprinting. Bioprinters can create living tissues and organs by layering bioinks containing cells. This groundbreaking technology holds immense potential for organ transplants, tissue engineering, and drug testing, revolutionizing the landscape of healthcare and saving countless lives.
Customized Prototyping and Product Development
In the realm of product development, 3D printing offers unparalleled advantages. Designers and engineers can quickly prototype and iterate their ideas, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods. This customization capability allows for the rapid development of prototypes tailored to specific design requirements.
Aerospace Innovations and Lightweight Structures
The aerospace industry has embraced 3D printing for creating lightweight and complex components. Aircraft parts can be designed with intricate geometries that were previously impossible, leading to reduced weight and enhanced fuel efficiency. This technology is driving innovation in the aerospace sector, enabling the production of high-performance components with increased functionality.
Architectural Marvels and Construction Advancements
In architecture and construction, 3D printing is reshaping the way structures are built. Large-scale 3D printers can create entire building components with precision. This not only expedites construction processes but also allows for the realization of architecturally ambitious designs. The technology is contributing to sustainable practices by minimizing waste and optimizing material usage.
Automotive Prototyping and Customization
The automotive industry benefits significantly from 3D printing for rapid prototyping and customization. Designers and engineers can create intricate components, test them for performance, and make necessary adjustments quickly. This flexibility in prototyping accelerates the product development cycle, leading to more efficient and customized automotive solutions.
Consumer Products and Personalized Manufacturing
3D printing has democratized manufacturing, enabling individuals to create custom and personalized products. From jewelry and accessories to home decor items, consumers can design and manufacture unique products tailored to their preferences. This shift towards personalized manufacturing is redefining consumer engagement and reducing the environmental impact of mass production.
Educational Tools and Prototyping in Academia
In educational settings, 3D printing serves as a valuable tool for hands-on learning and prototyping. Students can bring their ideas to life, understand complex concepts through tangible models, and gain practical experience in design and engineering. The accessibility of 3D printing technology in educational institutions fosters creativity and innovation among future generations.
Dental Applications and Prosthetics
The field of dentistry has embraced 3D printing for creating dental implants, crowns, and prosthetics. The technology allows for precise and patient-specific solutions, improving the accuracy and efficiency of dental procedures. Customized dental applications contribute to better patient outcomes and enhanced oral health care.
Artistic Expression and Sculptural Possibilities
Beyond the realms of technology and industry, 3D printing has become a medium for artistic expression. Artists and sculptors leverage the technology to bring intricate and avant-garde designs to life. The ability to create complex and detailed sculptures opens up new possibilities for artistic exploration and pushes the boundaries of what is achievable in the world of art.
Environmental Sustainability and Material Innovation
3D printing also plays a role in advancing environmental sustainability. The technology allows for the use of eco-friendly materials and reduces waste through efficient production processes. Material innovation in 3D printing contributes to the development of sustainable solutions, aligning with global efforts to create a more environmentally conscious manufacturing industry.
Conclusion: Shaping a 3D-Printed Future
The applications of 3D printing are diverse and continually expanding, influencing various industries and aspects of our lives. As technology evolves and becomes more accessible, the potential for innovation in manufacturing, healthcare, architecture, and beyond is limitless. 3D printing is truly shaping a future where customization, efficiency, and creativity converge.
To learn more about 3D printing applications, visit 3D printing applications.
